RCRA Update: Latest on Generator Improvements Adoption
September 2025 Update: New Hampshire
New Hampshire has adopted the Generator Improvements Rule, effective August 1, 2025. Revised regulations include new, more stringent requirements as well as new reliefs. Generators in the New Hampshire must abide by all State hazardous waste management requirements as well, including new state-specific rules that demand more than the Federal regulations.For example: New Hampshire adopted a new relief from the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule for waste generated during "episodic events" and added additional, state-specific requirements that eligible generators must follow in order to take advantage the newly adopted relief.
More Details
New Hampshire Rulemaking Env-HW 500, "Requirements for Hazardous Waste Generators"
Which States Adopted the Generator Improvements Rule?
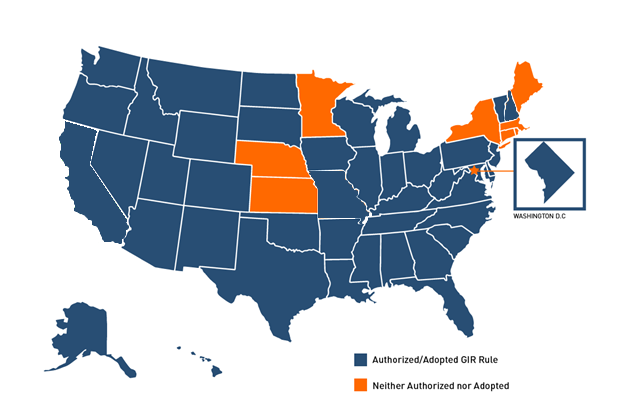
Where is the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule in Effect?
As of September 16, 2025, forty-two (42) states and Washington D.C. have adopted part or all of the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule. On the map above, states in blue have adopted (at least) the mandatory changes from EPA’s 2016 Final Rule.
That leaves only 8 states that have not yet adopted the Generator Improvements Rule (GIR):- Connecticut
- Kansas
- Maine
- Massachusetts
- Minnesota
- Nebraska
- New York
- Rhode Island
May 2025 Update: Missouri
The Missouri Department of Natural Resources (DNR) has updated their State hazardous waste regulations to incorporate substantial changes from the Federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) hazardous waste standards, by reference, as of July 1, 2024, including the Generator Improvements Rule and several other RCRA rulemakings.
More Details
Missouri Updates State Hazardous Waste Standards for Generators
January 2025 Update: New York
The Generator Improvements Rule or "GIR" is one of many RCRA rulemakings that the New York State Department of Environmental Conservation (NYSDEC) may adopt into the State's regulations.
NYSDEC must adopt all provisions of the GIR that are more stringent than the current State hazardous waste standards. More stringent provisions include new rules for marking containers, expanded contingency planning requirements, and a re-notification requirement for small quantity generators (SQGs). As for new reliefs added by the GIR, NYSDEC may decide to add allowances for "episodic events," consolidation of hazardous waste at larger generator sites, and more.
Other Federal RCRA rulemakings being considered for adoption in New York, all of which EPA finalized between 2013 and 2020, include new management standards for hazardous waste pharmaceuticals ("Subpart P"), relief for solvent-contaminated wipes, updates related to electronic hazardous waste manifests (e-Manifests), and more.
In mid-2023, DEC revised New York's hazardous waste regulations by adding paint and aerosol cans to the state universal waste program.
More Details
NYSDEC: "Revisions Under Consideration"
NYSDEC: Generator Improvements Rule Summary
July 2024 Update: California
The hazardous waste Generator Improvements Rule (GIR) is in effect in California as of July 1, 2024. California DTSC adopted more stringent requirements for generators and re-organized the state code of regulations to align it with Federal RCRA requirements for hazardous waste management.
Cheat SheetThe California "Generator Improvements Rule" cheat sheet available here highlights 7 key rule changes for hazardous waste generators in effect as of July 1, 2024.
For Members
- Member Bulletin: California Generator Improvements Rule
- Recorded Webinar: California Generator Improvements Rule (45 min.)
March 2023 Update #1: Washington, D.C.
Environmental regulators in Washington, D.C. have adopted EPA’s Generator Improvements Rule into the District’s hazardous waste regulations. D.C. adopted the rule in full—adding new, stricter provisions for contingency planning, re-notification, and more, as well as new reliefs such as the counting exemption for waste generated by episodic events.
- The revised requirements took effect immediately on January 20, 2023.
With new regulations in effect now, hazardous waste generators in the District of Columbia must comply with detailed new provisions and take up new responsibilities.
March 2023 Update #2: California
California’s Department of Toxic Substances Control (DTSC) proposed a rule to adopt several more-stringent provisions for hazardous waste generators from the Generator Improvements Rule.
A 45-day public comment period opened on Friday, March 24 and closes on May 8. Generators, industry stakeholders, and the general public can submit written comments in two ways:- Email written comments to regs@dtsc.gov
- Mail hard-copy written comments to DTSC
See the seven stricter requirements California is proposing for adoption in our blog dedicated to DTSC's proposed rule, just published here.
What Does “Authorized” Mean?
US EPA authorizes most states to oversee a state-level hazardous waste program, provided that the state maintains requirements that are at least as stringent as the Federal RCRA regulations.
When a state updates its program, they must submit the changes to US EPA for approval. When EPA gives its final authorization, they officially hand off enforcement powers for those provisions to the state. EPA provides more info about State Authorization on this web page.
New RCRA Rules Under Construction...
All of these states still must adopt overhauled RCRA standards from US EPA's Generator Improvements Rule.
- Connecticut is actively working with US EPA and expects to adopt the Generator Improvements within one year.
- Kansas is working to adopt updates to the Federal hazardous waste regulations, including the Generator Improvements Rule, the Hazardous Waste Pharmaceuticals Rule, and other rulemakings.
- Maine expects to start drafting changes to its state hazardous waste management rules soon—including adoption of the Generator Improvements Rule and the Hazardous Waste Pharmaceuticals Rule.
- Massachusetts plans to propose a timeline for adopting the Generator Improvements before taking further action.
- Minnesota now plans to publish Land-Related Housekeeping Amendments with a formal public comment period. Minnesota will adopt some of the voluntary (i.e., more flexible) provisions from the GIR. Currently, the state does not plan to adopt the allowance for consolidation of VSQG waste nor the relief for episodic generation, however.
- Nebraska is in the process of adopting the Generator Improvements Rule in its entirety, with no precise timeline for implementation.
- New York will incorporate the GIR into its state regulations as part of an ongoing rulemaking project titled FedReg6, which also includes the Hazardous Waste Pharmaceuticals Rule, revisions to the Definition of Solid Waste, and relaxed management standards for airbags.
- Rhode Island is working through state-specific issues with EPA before adopting the updated RCRA rules. Both states plan to adopt at least the mandatory provisions.
Older Generator Improvements Rule Updates (Pre-2023)
Update: November 7, 2022
- 39 states, and Washington, D.C., have adopted overhauled hazardous waste management regulations from US EPA’s Generator Improvements Rule. Generators in many states (and Guam), meanwhile, are still waiting for the overhauled, re-organized RCRA requirements to be adopted:
California, Connecticut, Kansas, Maine, Massachusetts, Minnesota,Missouri, Nebraska,New Hampshire, New York, and Rhode Island.
Update 05/15/2022 (Montana)
- Montana has incorporated-by-reference revised RCRA regulations, including the Generator Improvements Rule provisions, effective May 14, 2022.
Update 02/03/2022 (Vermont, Texas)
- In Vermont, the Generator Improvements Rule provisions are among changes to the hazardous waste regulations that took effect on February 1, 2022.
-
In Texas, final action to adopt EPA's Generator Improvements Rule and make other significant changes to the state hazardous and industrial waste regulations took effect on Feb. 3, 2022.
Update 12/23/2021 (Oregon)
- Oregon DEQ approved major changes to the state's hazardous waste regulations. Updated rules for hazardous waste generators include the adoption of landmark updates from US EPA's Generator Improvements Rule. Also coming to Oregon: New management standards for hazardous waste pharmaceuticals, aerosols as universal waste and more. The new regulations take effect January 1, 2022.
Update 06/14/21 (Maryland)
- Maryland has adopted the RCRA Hazardous Waste Generator Improvements Rule. A Notice of Final Action was published to the Maryland Register issued on April 23, 2021 (pp. 359—360). When the rule was proposed, Maryland DOE released a two-page document detailing critical hazardous waste regulatory changes. Effective date: May 3, 2021.
Update 04/30/21 (Tennessee)
- Tennessee has adopted the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule, along with other Federal hazardous waste rule updates. Effective date: May 13, 2021.
Update 01/21/20 (Delaware)
- Effective January 21, 2021, Delaware has adopted the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule. New regulations concerning aerosols as universal waste, hazardous waste pharmaceuticals, waste airbags, hazardous waste import/export, and electronic Manifests are in effect now in Delaware too.
Update 01/13/20 (Nevada)
- Nevada adopted the Generator Improvements Rule in 2020, Lion has learned. The updated hazardous waste regulations were signed into law on August 25, 2020.
Update 11/18/20 (Arkansas)
- As of October 2, 2020, Arkansas has adopted five recent RCRA rule updates, including the Generator Improvements Rule, into state Regulation 23. The state's Pollution Control and Ecology Commission (APC&EC) notified stakeholders of the rulemaking by e-mail this week.
Update 10/05/20 (Michigan, Ohio, Wisconsin)
- Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin have all incorporated the RCRA Generator Improvements Rule into their state hazardous waste regulations. Effective dates:
Update 7/28/20 (Louisiana, North Dakota)
- Louisiana and North Dakota each adopted the updates in EPA's Generator Improvements Rule in July 2020,
Update 5/19/20 (Indiana, Wyoming)
- Indiana and Wyoming are the two states to most recently adopt EPA's Generator Improvements Rule. That means half the country (25 states) have now adopted the more stringent RCRA requirements.
What is the Generator Improvements Rule?
The effective date for US EPA’s landmark Generator Improvements Rule (GIR) was May 30, 2017. All US States with approved RCRA programs must adopt at least the more-stringent regulations from the GIR. If a state needs to change its state law to accommodate changes to its hazardous waste program, the law allows additional time. That said, new Federal rules are meant to be adopted by authorized states within a 1 to 2 year time frame.
The 1-year and 2-year deadlines are now long passed. If your state has not yet adopted the mandatory elements of the Generator Improvements Rule, you should expect them to very soon.
How the Generator Improvements Rule Makes RCRA Stricter
The following are examples (not all-inclusive) of more stringent requirements from EPA's Generator Improvements Rule:
Waste Determinations
-
The recordkeeping and retention requirements for hazardous waste determinations previously found at 40 CFR section 262.40(c) were moved into section 262.11(f), with clarifications on what records must be kept;
-
Small and Large quantity generators must indicate waste codes on containers before shipping hazardous waste off site to a RCRA permitted treatment, storage, and disposal facility in accordance with the requirements of 40 CFR section 262.32; and
-
Any generator managing a potentially hazardous waste should manage it in accordance with the generator regulations until such time that the generator is sure that the waste is not hazardous (e.g. while awaiting the results of analysis).
Marking and Labeling
- The final rule added a provision for generators to mark hazardous waste containers with an indication of the hazards of the contents.
Emergency Preparedness and Prevention
- The GIR added a requirement that the generator must keep documentation of the fact that it has made arrangements with local emergency responders. LQG’s written contingency plan must include satellite accumulation areas and have a “quick reference guide.”
Facility Closure
- There are new closure reporting requirements for a large quantity generator’s 90-day central storage area.
Renotification for Small Quantity Generators (SQGs)
- Small quantity generators will be required to re-notify starting in 2021 and every four years thereafter using EPA Form 8700-12. This re-notification must be submitted by September 1st of each year in which re-notifications are required.
Watch your State Registers for official notification of when the GIR has been adopted in your state, keep an eye on Lion News for more updates in the future, or visit the EPA website for a list of state adoption activities.
Did Your State Adopt the Generator Improvements Rule?
If your state is pictured in blue on the map above, check your state regulations to see if they adopted the GIR in its entirety. States are not required to adopt anything that is less stringent then their current regulations.
New RCRA rules that are less stringent include:
-
Allowing a hazardous waste generator to avoid increased burden of a higher generator status when generating episodic waste provided the episodic waste is properly managed
-
Allowing a very small quantity generator (VSQG) to send its hazardous waste to a large quantity generator under control of the same person
-
Venting containers at satellite areas for certain conditions
-
Removing the need for the home address of Emergency Coordinators
To check your updated state regulations, click here and scroll to your state for the link: Links to Generator Improvements State Regulations.

What if My State Did Not Adopt the Generator Improvements Rule?
In states that have not yet adopted the Generator Improvements Rule, Lion recommends that generators comply with the stricter regulations.
In the US, hazardous waste regulation is a joint effort between Federal and state agencies. When US EPA makes changes to the Federal program, states must adopt any updates that make the rules more stringent. States that fail to maintain hazardous waste regulations that are at least as stringent as the Federal RCRA program risk losing their authorization to run a state program.
Get RCRA Training—When You Want, Where You Want
US EPA requires hazardous waste professionals to complete annual training on the RCRA requirements. Lion makes it easy to meet your RCRA training mandate in a variety of formats—nationwide public workshops, convenient online courses, live webinars, and on-site training.
Browse RCRA training options here to find the course that fits your needs, your schedule, and your learning style.
Federal Generator Improvements Rules Coming to Every State
Sign up for Lion News, get the guide right in your email inbox.News and insights delivered to your inbox weekly.
View our Terms and Privacy Policy.
Find a Post
Recent Posts
Compliance Archives
Download Our Latest Whitepaper
Tips to identify and manage universal waste under more-stringent state regulations for generators and universal waste handlers in California.

By submitting your phone number, you agree to receive recurring marketing and training text messages. Consent to receive text messages is not required for any purchases. Text STOP at any time to cancel. Message and data rates may apply. View our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy.
